If you’re from a manufacturing background, you’re almost certain to be familiar with Industry 4.0. Apart from its reputation as cutting-edge technology for manufacturing and quality assurance, AR has garnered considerable attention in repair and maintenance scenarios, even outside the manufacturing industry, which served as its foundation. The commercial use cases for AR were expected to receive over 4.1 Billion USD in 2024.
Now, let’s examine why AR captures the imaginations of maintenance and repair managers worldwide and whether its disadvantages deter them from pursuing the initiative.
How does augmented reality work in repair and maintenance?
The primary function of an AR application is to simplify the life of a service technician by providing them with all necessary maintenance/repair data for a particular service case. The application accomplishes this by performing the following steps:
Step 1: Identify the equipment (or a problem with it)
Technicians use augmented reality applications installed on mobile devices or smart glasses/headsets to maintain the equipment. While smart glasses enable hands-free access to necessary data, mobile devices, particularly tablets, provide a wider field of vision and are more affordable.
Regardless of the device on which it is installed, the repair and maintenance augmented reality app utilises image recognition to compare the camera’s live feed to a large database of related images. This way, it automatically determines the equipment’s model or the source of the problem.
Step 2: Collecting pertinent augmented reality data about the identified issue/equipment
After identifying the equipment or issue, the app immediately accesses all augmented reality data (tips, scenario steps, voiced guide, etc.) associated with that model or issue. Nota bene: In the case of routine maintenance or repairs performed by an experienced technician who is confident in manually selecting the equipment/problem from the app’s menu, this step can serve as a jumping-off point.
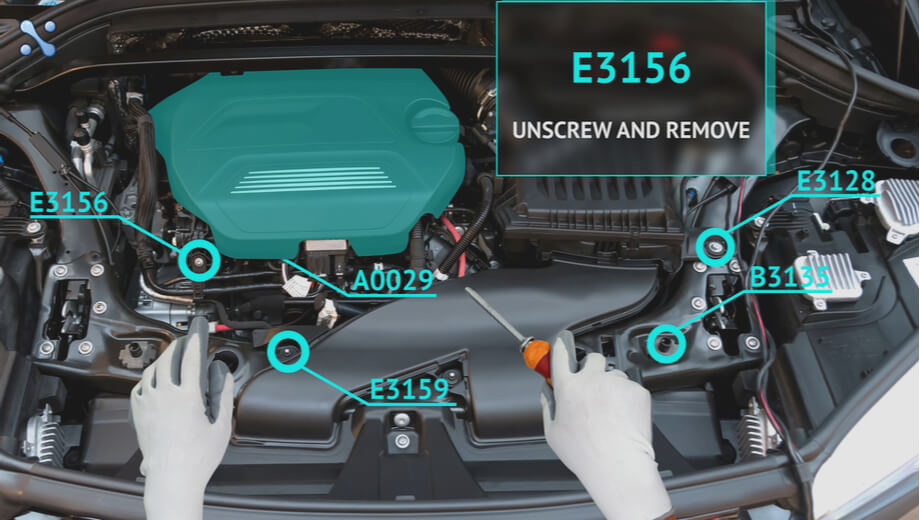
Step 3: Real-time augmentation of camera feed with augmented reality content
The augmented reality app utilizes image recognition algorithms to dynamically augment live camera feeds (with equipment in focus) with a variety of content types, including:
– Text and/or graphic elements (technical documentation and manuals)
– Video clips (see an example here).
– Three-dimensional objects.
Clearly, 3D objects and videos are the most effective visual aids, particularly when it comes to complex equipment manipulations. Simple text and images, on the other hand, can be extremely useful in less elaborate service scenarios.
Additionally, augmented reality apps provide technicians with a comprehensive list of actions (accompanied by animations or illustrations) that guide them through the entire service process.
Additional capabilities
Apart from the augmented reality functionality, maintenance apps may include an integrated video communication feature. Technicians can consult an expert via video call while demonstrating the serviced equipment using Skype, Zoom, Microsoft Teams, or any other VoIP messenger integrated with the AR app.
Additionally, the speech-to-text feature can be beneficial. It enables technicians to take notes during the service process without impeding it with a smartphone or notepad.
Key industries benefiting from AR in repair and maintenance
There are multiple industries that are benefiting from AR in repair and maintenance and many of them are listed as follows:
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Manufacturing
- Oil and Gas
- Utilities

AR advantages in terms of repair and maintenance
Rather than spending considerable time investigating each complex repair case, you can use an augmented reality repair app to:
- Increase equipment uptime by reducing mean time to repair and improving the quality of maintenance -> significantly lower downtime costs.
- Increase your field service technicians’ first-time-fix rates -> eliminate operational costs associated with unnecessary travel.
- Reduce technician training time -> lower employee onboarding costs.
- Provide self-service repair and maintenance to your customers -> reduce associated operational costs and field service wait times.
All of these benefits naturally result in an increase in service quality and customer satisfaction, which can be leveraged to create a stellar competitive advantage with some marketing and sales efforts.
AR applications and challenges in repair and maintenance
Here are some companies that are already utilizing augmented reality apps for repair and maintenance, along with the results they have obtained:
- Bosch – automotive repair (reported a 15 percent fix-time decrease for simple car repairs).
- ThyssenKrupp – elevator repair (reported a 75 percent decrease in service time overall).
- Huawei – repair of DC-to-AC solar inverters (reported a significant reduction in technicians’ cognitive load and a reduction in service time).
However, as amazing as these use cases are, implementing an augmented reality application is not without its challenges:
- Employees’ reluctance to adapt to such cutting-edge technology as augmented reality may slow app adoption, especially if you opt for smart glasses (but this is easily remedied with a motivation strategy and employee training).
- Preparing augmented reality content can take an inordinate amount of time and money, but you cannot skimp on it because, at the end of the day, your augmented reality application is only as good as your data. However, our 3D designers and business analysts have a few tricks up their sleeves for expediting the content preparation process (e.g., using computer-aided design data that you can get from your product engineering team).
As you can see, the magnitude of the challenges does not outweigh the benefits of an augmented reality solution.
Future Trends in AR integrated Repair and Maintenance

Key aspects of these future trends:
Predictive Maintenance with AI and IoT
AR systems will integrate smoothly with AI and IoT sensors to deliver real-time insights into machine health, enabling technicians to proactively spot potential issues and carry out preventative maintenance before any breakdowns happen.
Enhanced Remote Assistance
Experts from anywhere in the world can assist on-site technicians through intricate repairs using live AR overlays, offering real-time instructions and visual support.
Haptic Feedback in Training
AR training simulations will include haptic feedback to provide technicians with a more authentic hands-on experience, enhancing muscle memory and skill acquisition.
Advanced Wearable AR Devices
The next generation of AR glasses will feature better visual quality, a broader field of view, and more intuitive interaction methods, allowing for hands-free operation during maintenance tasks.
Data Visualization and Analytics
AR will display complex maintenance data in user-friendly visual formats, such as overlays of charts and graphs directly on the equipment, making interpretation and decision-making easier.
Personalized Training and Guidance
AR systems will tailor instructions and visual cues to match individual technician skill levels, ensuring that everyone gets the right amount of support.
Spatial Computing Integration
By leveraging spatial computing technology, technicians will be able to manipulate and visualize 3D models of equipment within their work environment, deepening their understanding of complex assemblies.
Augmented Reality for Complex Environments
AR applications will be designed for challenging settings like confined spaces or hazardous areas, offering visual guidance and safety measures to technicians.
Reduced Downtime
By facilitating quicker troubleshooting and preventative maintenance, AR can greatly reduce equipment downtime and enhance operational efficiency.
Improved Technician Productivity
AR overlays and real-time instructions can significantly boost technician productivity.
How can Neuronimbus Help you with Augmented Reality Solutions?
Neuronimbus offers cutting-edge AR solutions tailored for repair and maintenance, integrating AI, IoT, and digital twin technology to enhance efficiency. Our custom AR applications provide real-time troubleshooting, remote assistance, 3D visualization, and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and improving technician productivity.
With interactive UI/UX design, AR-powered training simulations, and scalable enterprise integration, we ensure seamless adoption and maximum ROI. Whether through smart glasses, mobile devices, or cloud-based platforms, our solutions empower businesses to optimize maintenance operations, lower costs, and enhance service quality. Partner with Neuronimbus to transform your AR-driven maintenance strategies with cutting-edge digital innovation.
FAQs About Augmented Reality App Development for Repair and Maintenance
Q. What is Augmented Reality (AR) in repair and maintenance?
A. AR in repair and maintenance involves using AR technology, typically through apps, to assist technicians in identifying and resolving equipment issues more efficiently by providing real-time, augmented visual guidance and information.
Q. How does an AR app work in the field of maintenance?
A. AR apps in maintenance work by recognizing equipment through image recognition, providing relevant data and instructions, and overlaying digital information or graphics onto real-world images to guide technicians through repair processes.
Q. What devices are commonly used for AR in maintenance?
A. Common devices for AR in maintenance include smartphones, tablets, and smart glasses or headsets, each offering different advantages like hands-free operation or wider display fields.
Q. What are the key features of AR apps in repair scenarios?
A. Key features include image recognition for equipment identification, real-time data overlay, 3D object visualization, step-by-step interactive guides, and video communication capabilities for remote expert consultations.
Q. Can AR apps in maintenance reduce repair times?
A. Yes, AR apps can significantly reduce repair times by providing quick and accurate guidance, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing equipment downtime.
Q. What are the benefits of using AR for equipment maintenance?
A. Benefits include increased equipment uptime, improved first-time fix rates, reduced technician training time, potential for customer self-service, and overall cost reductions in maintenance operations.
Q. How does AR technology impact technician training?
A. AR technology can significantly reduce technician training time by providing interactive, on-the-job training tools that enhance learning and retention compared to traditional methods.
Q. Can AR apps be used for customer self-service in maintenance?
A. Yes, AR apps can be designed to enable customers to perform certain maintenance tasks themselves, reducing wait times and operational costs for service providers.
Q. What challenges might companies face in implementing AR for maintenance?
A. Challenges include employee resistance to new technology, especially smart glasses, and the time and resources needed to prepare effective AR content.
Q. How can businesses overcome the challenges of AR app development?
A. Businesses can overcome these challenges with proper motivation strategies, employee training, and by streamlining AR content preparation, possibly using existing CAD data.